Researchers at security firm Cofense discovered a phishing campaign in which criminals steal victims’ credentials by abusing Telegram’s API. Bad actors created malicious domains that helped them bypass security tools.
This phishing attack started in mid-December 2020 but since then it stopped. The targets who received malicious emails mainly worked in the U.K. financial services sector.
Telegram, a popular messaging app with more than 500 million monthly active users, is attractive to privacy-mindful users because of its end-to-end encryption and newly announced message self-destruct options. For the same reasons, however, it is also appealing to threat actors.
In addition to the standard messaging application, Telegram also offers an API that allows users to create programs that use Telegram chats as an interface.
The hackers used the APIs to create realistic-looking phishing domains that fooled security checks.
“For this particular campaign, they spoofed an email account that appeared to an internal user as legitimate,” says Cofence’s threat analyst, Jake Longden. “Then they used a domain as the site for the URL redirection that most likely at the time wasn’t a known bad site, but which is now classified as malicious.”
The Attacks
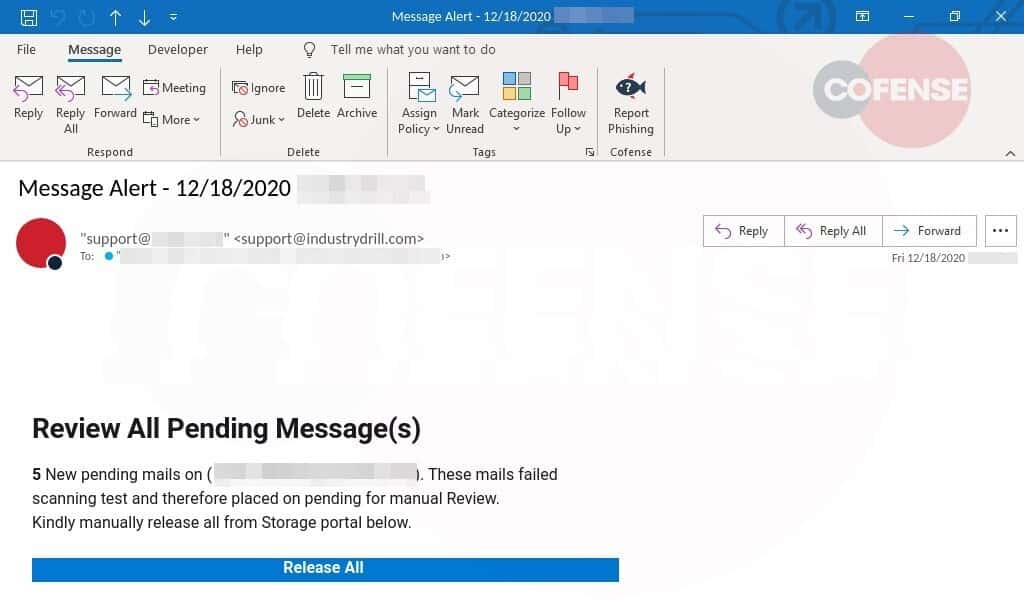
The victims received phishing emails from a sender with an internal domain, an address like “team@internal.com.” Emails actually came from a source outside the organization, according to the researchers.
When the victim clicked the link, they are taken to an attacker’s website that had been created using Telegram API and looked like a webmail login page.
Any credentials that the victim entered were harvested, and the data was sent to the Telegram API of the criminals.
The threat actor took measures to circumvent interference with the help of the Telegram API. “They’re complicating methods for removing stored credentials that have been harvested, and can view and access these credentials at their convenience on a page they control,” the report says.