The threat actor who stole over $600 million worth of cryptocurrency assets is now returning the funds.
The hacker stole $611 million worth of cryptocurrency from the Poly Network earlier this week in what was called the biggest cryptocurrency heist in history. The stolen funds included $273 million in Ethereum tokens, $253 million in Binance Smart Chain, and $85 million in Polygon Network (in USDC).
The attacker has already sent over $256 million worth of Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and USD Coin tokens to the network. The hacker has to send another $269 million to return all the funds.
As Elliptic Chief Scientist and Co-founder Tom Robinson found, the threat actor explained their motivation behind the hack by embedding Q&A messages in transactions of the stolen cryptocurrency. But they offered no explanation for the roundabout.
But experts from the industry speculate the incident was most likely triggered by crypto cybersecurity company SlowMist’s claim that it tracked down the attacker’s email address, IP address, and device fingerprint.
SlowMist discovered that the attacker used Monero (XMR) to fund their attack. The assets were exchanged to BNB, ETH, MATIC, and other tokens.
Poly Network asked the hacker to return the stolen tokens to avoid getting caught on law enforcers’ radar:
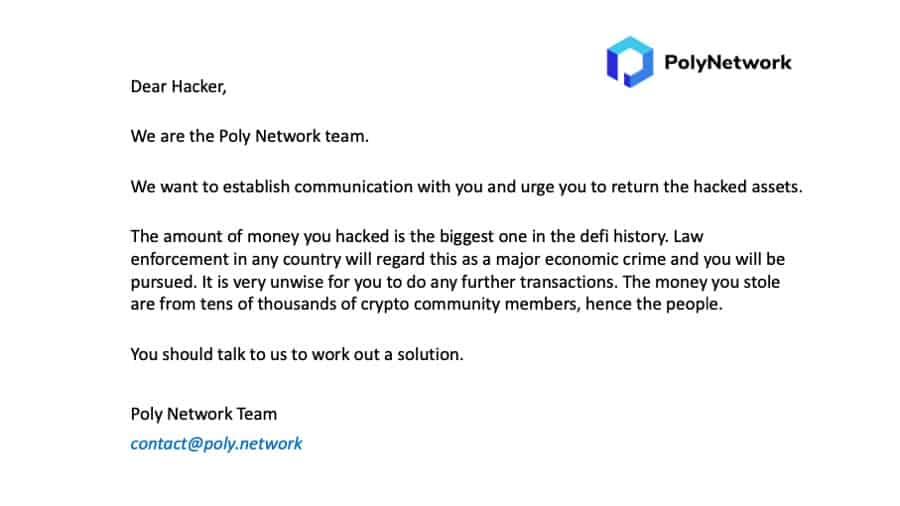
In a tweet, Poly Network stated the same: “We call on miners of affected blockchain and crypto exchanges to blacklist tokens coming from the above addresses. @Tether_to @circlepay.” “We will take legal actions and we urge the hackers to return the assets.”
The crypto cybersecurity company said the attacker exploited a vulnerability in the contract calls that allowed them to gain control of funds and transfer them to their wallets.
“This attack is mainly because the keeper of the EthCrossChainData contract can be modified by the EthCrossChainManager contract, and the verifyHeaderAndExecuteTx function of the EthCrossChainManager contract can execute the data passed in by the user through the _executeCrossChainTx function,” SlowMist explained. “Therefore, the attacker uses this function to pass in carefully constructed data to modify the keeper of the EthCrossChainData contract.”







